

|
Manual |
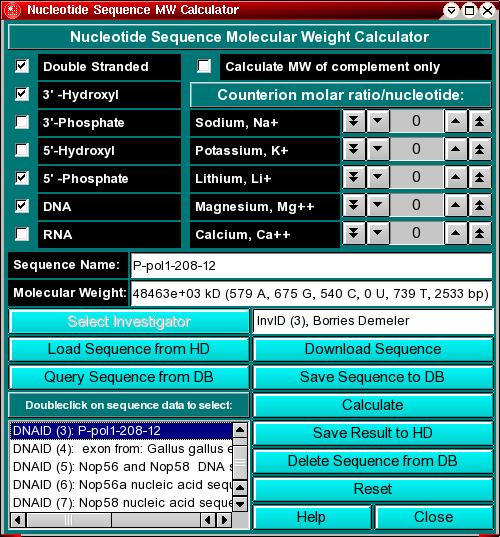
This program allows you to calculate the molecular weight of DNA and RNA molecules from sequence files which are written in the Genbank format (text format). The program can be used to calculate single- or double stranded sequences, or the molecular weight of the complement of a sequence. You can select the 3' and 5' terminus chemistry, and add common counterions in molar ratios to each residue.
Note: This program will utilize the database backend of UltraScan. This functionality allows you to save certain files and data in a database, among them the nucleotide files analyzed with this module. If the database system is not supported or available on your system, you will get a warning message when opening this module.
You can download DNA/RNA sequences directly into the calculator from Genbank. Clicking on the "Download Sequence" button will connect you to the Entrez database for downloading Genbank sequence files.
If you would like to import your own sequence, you need to make sure that the file is in the proper Genbank format.
Example sequence:
DEFINITION exon from: Gallus gallus egg white lysozyme gene, partial cds. ORIGIN 1 agtcccgctg tgtgtacgac actggcaaca tgaggtcttt gctaatcttg gtgctttgct 61 tcctgcccct ggctgctctg gggaaagtct ttggacgatg tgagctggca gcggctatga 121 agcgtcacgg acttgataac tatcggggat acagcctggg aaact //
The following four fields are required:
Field 1: "DEFINITION"
This field has to be spelled in upper case and everything following
it on the same line will be printed as the sequence title in the program.
Field 2: "ORIGIN"
This field has to be spelled in upper case and should be the only word in this
line. This word indicates that the next line will contain the beginning
of the actual sequence.
Field 3: The actual sequence (multiline). The sequence elements (a, g, c, t, u) can be spelled in upper or lower case, and can contain spaces. Each line with sequence data needs to contain exactly one string, separated by white space, in front of the actual sequence data. This is ordinarily the position of the first residue listed in that line.
Field 4: The sequence terminator "//". This terminator symbol should be on a separate line following the last sequence line. Any information past the terminator symbol is ignored.
Amy other information contained in the file is ignored.
The program uses the following algorithm (Ref.: Steve Hardies, University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, Dept. of Biochemistry):
Natural isotope adjusted MWs C 12.011 N 14.0067 O 15.9994 H 1.00794 P 30.9738 Adenine C5N5H5 Guanine C5N5OH5 Thymine C5N2O2H6 Cytosine C4N3OH5 Uracil C4N2O2H4 ribose C5O5H10 deoxyribose C5O4H10 phosphate PO4 Adding the base to the ribose involves loss of 1 H2O Bonding the phosphate to either 5' or 3' OH causes loss of 1 HO An internal ribonucleotide is then calculated as base+ribose+phosphate -H2O - 2 OH. MW of an internal ribonucleotide: dA - 313.21 dC - 289.19 dU - 290.17 dG - 329.21 dT - 304.63 to make RNA, add 15.99 for each nucleotide to make terminal 3' OH add 17.01 to make terminal 3' phosphate add 94.97 to make terminal 5' phosphate - no change to make terminal 5' OH subtract 77.96 Does not account for the 2nd dissociable H of the terminal phosphate, which has a pK somewhere around neutrality. It would be 7.2 for a free phosphate.
Explanation for fields and buttons:
|
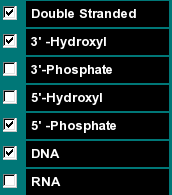
This group of functions allows you to select if the selected molecule is to be calculated as an RNA or DNA molecule, if the molecular weight of the sequence should be calculated including the molecular weight of the complement (in that case select "Double Stranded"), and what groups are on the 3' and 5' termini of the sequence. |

|
If this option is selected, the complementary sequence will be generated, and the molecular weight of the complement only will be reported. |

|
By clicking on the arrow buttons (single arrow: steps of 0.01, double arrow: steps of 0.1) you can select the molar ratio of counterions per nucleotide of the sequence. For example, if you selected a sodium ratio of 0.01, one in a 100 nucleotides of the sequence would be considered as having one sodium ion bound, and the weight of that ion would be added to the total molecular weight. If the sequence contained less than a hundred nucleotides, the corresponding fractional molecular weight of a sodium ion would be added to the reported molecular weight. |

|
These fields show the first line of the sequence identification listed in the sequence file, as well as the molecular weight and sequence composition. If you are loading a DNA sequence, but selected the "RNA" option above, an warning message will be shown. An equivalent error message is shown if you selected "DNA" but loaded an RNA sequence. |

|
|
|
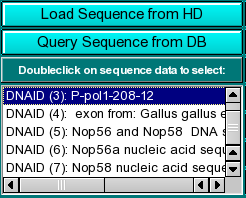
Sequence Loading: You can load sequences into this program by one of two methods:
|

|
|
This document is part of the UltraScan Software Documentation
distribution.
Copyright © notice.
The latest version of this document can always be found at:
Last modified on January 12, 2003.